Degree of Dissociation Formula
Following Wikipedias van t Hoff factor discussion the van t Hoff factor can be computed from the degree of ionization as follows. The law holds good only for weak electrolytes and fails completely in the case of strong electrolytes.
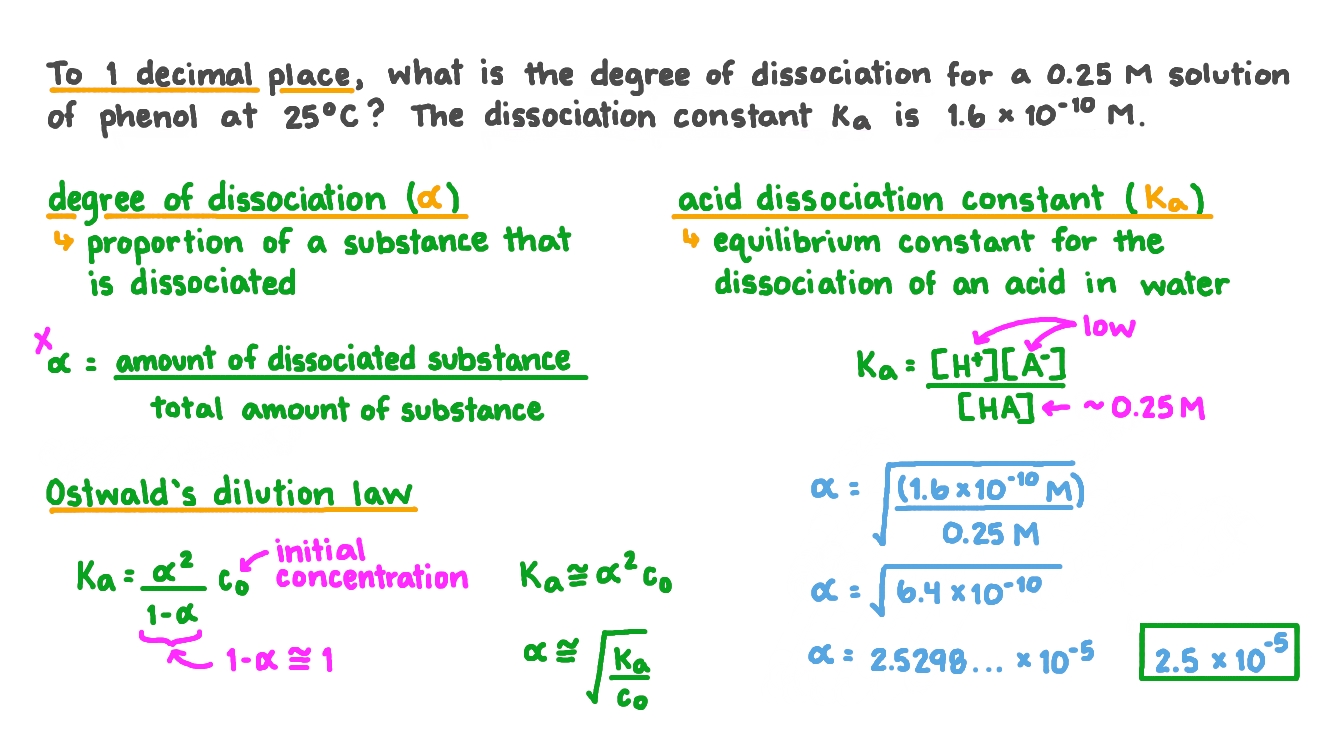
Question Video Calculating The Degree Of Dissociation Of A Solution Of Phenol Given The Acid Dissociation Constant Nagwa
The degree of dissociation often represented by the symbol 𝛼 is the proportion of a substance that is dissociated.

. Explain the effect of change of pressure on Equilibrium. For example when a field of 200 kVcm is applied α CH 3 COOH increases by 12. The total pressure at equilibrium is 1 atm.
In case of dissociation quantity of solute increases colligative property increases molar mass of solute decreases. Electrochemistry is the study of chemical processes which lead to electrons moving. Percent Dissociation Formula - The ratio of the concentration of the dissociated hydrogen ion H to the concentration of the undissociated species HA is represented by the symbol α alpha.
The degree of dissociation 𝛼 is typically presented as a decimal so we can convert the percentage of dissociation to a decimal. The degree of ionization or dissociation α of week electrolyte increases with dilution and law of mass action can be applied to them. Click hereto get an answer to your question Calculate the degree of dissociation alpha of acetic acid if its molar conductivity m is 3905 Scm2mol-1 Given lambdao H- 1 3496Scm2mol- 1lambdao CH3COO 409Scm2mol- 1.
So the Vant Hoff factorRead More. X Y 2 1 X 2 0 2 Y 0 with initial number of moles At equilibrium 1 α α 2 α. I 1 αn - 1.
What is Van t Hoff factor for complete dissociation. The degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte E increases when a strong electric field with the strength E is applied to a solution of this electrolyte. As the solution is saturated but infinitely dilute.
If degree of dissociation of NH 3 is 75 then calculate the partial pressure of each gas at equilibrium. Therefore total number of moles is 1 α α 2 α 1 2 α. Assume 1 𝛼 1.
Dissociation in chemistry and biochemistry is a general mechanism in which typically in a reversible way molecules or ionic compounds such as salts or complexes differentiate or break. Let us consider that at t 0 moles of NH 3 a moles of N 2 0 and moles of H 2 0. We could plug this value into the equation above but the question includes one extra detail.
Now suppose you have a reaction like this ceA-B C The initial state of A is always the concentration of A should be given in the question while initial moles of B and C are zero if anything else is not specified. In this video you will learn about the degree of dissociation and dissociation constant it will also help you to understand the formula and numerical based. M is the observed molar mass.
0 1 4 7. Application of Ostwalds dilution law i It is useful in the calculation of the dissociation constant K of the weak acids and weak base by determining the degree of dissociation α from conductance. Download our Android app at httpsgoogl5JM1G2For Unedited raw footage ask in comment boxCepek media private Limited.
The degree of dissociation of PCl 5 at a certain temperature and under atmospheric pressure is 02. In the calculation of the degree of dissociation. The change in the degree of dissociation of the electrolyte is monitored by a change in the electric.
M O b s e r v e d M. M 1 2 α 1 164 656. In the calculation of solubility of a sparingly soluble salt.
4 7 1 0 0 0. For dissociation in absence of association the value of i is greater than 1. 2 N H 3 g N 2 g 3 H 2 g Solution.
Where α is the degree of dissociation. It is defined as the product of the initial concentration of the reactant and the degree of dissociation. If α is the degree of dissociation then at.
Hence Where u are ionic mobilities at infinite dilution. Limitations of Ostwalds Dilution law. Calculate the pressure at which it will be half dissociated at the same temperature.
Strong electrolytes have a degree of dissociation close to one while weak electrolytes have a degree of dissociation less than one. Thus degree of dissociation of a weak electrolyte is proportional to the square root of dilution. I αn 1 - α where α is the degree of dissociation and n equals the number of ions formed from one formula unit of the substance.
It is denoted by i. Complete step by step answer. Degree of ionization increases on dilution.
The degree of dissociation is the phenomenon of producing free ions carrying current which at a given concentration is dissociated from the fraction of solute. The formula above is often rearranged as follows. I N o r m a l M.
The degree of dissociation can be calculated by dividing the amount of the dissociated substance by the total amount of substance where the amount can be given as the number of molecules or moles.
Degree Of Dissociation Pka Of Weak Acid Calistry

A Calculate The Degree Of Dissociation Of 0 0024 M Acetic Acid If Conductivity Of This Solution Youtube

Calculate The Degree Of Dissociation Of Hi At 450 C If The Equilibrium Constant For The Diss Youtube

Calculate The Percentage Degree Of Dissociation Of An Electrolyte Xy 2 Normal Molar M Youtube
Comments
Post a Comment